What Are Natural Gas Liquids – NGL?
Natural gas liquids (NGL) are components of natural gas that are separated from the gas state in the form of liquids. This separation occurs in a field facility or a gas processing plant through absorption, condensation or other methods. Natural gas liquids are classified based on their vapor pressure:
 Understanding Natural Gas Liquids
Understanding Natural Gas Liquids
NGLs are valuable as separate products, and it is, therefore, profitable to remove them from the natural gas. The liquids are first extracted from the natural gas and later separated into different components.
Natural gas liquids are hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a molecule composed exclusively of carbon and hydrogen. As hydrocarbons, NGLs belong in the same family of molecules as do natural gas and crude oil.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Natural gas liquids (NGLs) are components of natural gas that are separated from the gas state in the form of liquids.
Applications for NGLs include cooking, heating, plastics, and fuels.
NGLs can be expensive to handle, store, and transport.
The U.S. has a growing export production of NGL.
Types of NGLs and Their Applications
The chemical compositions of NGLs are similar, but their applications vary widely. There are many uses for NGLs including cooking, space heating, and blended into fuels for vehicles.
Ethane
Applications include plastics production and petrochemical feedstock—raw materials fed into an industrial production process to yield a different end product. End-use products include plastics, plastic bags, antifreeze, and detergent.
Propane
Applications and uses include residential and commercial heating, cooking fuel, small stoves, and petrochemical feedstock. Some vehicles also use propane as fuel.
Butanes
Butanes can be blended with gasoline and propane. Products include synthetic rubber for tires and lighter fuel. In its purest form, butane is useful as a refrigerant. Combined with propane it becomes liquified petroleum gas (LPG).
Isobutanes
Industrial use can include refinery feedstock and petrochemical feedstock. End-use products include aerosols and refrigerants.
Pentanes
Pentanes are used in natural gasoline and as a blowing agent for polystyrene foam. Pentanes plus, a special category also known as natural gasoline, is blended with vehicle fuel and exported for bitumen production in oil sands. Natural gas is pumped into heavy crude oil reserves allowing it to flow easier.
Challenges and Opportunities
The U.S. shale boom increased extraction rates of NGLs. NGL extraction is positively related to the price of crude oil. As the market price of crude decreases, oil, gas, and chemical companies expand their offerings to include NGLs and offset lost revenue.
In the last 10 years, there have been significant advancements in technologies such as horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing techniques, which involve using high pressured water or liquids to extract gas. As a result, NGL production has increased steadily. NGLs provide natural gas producers with an additional income stream, which can help diversify their revenue.
A challenge with NGLs is that they're expensive to handle, store, and transport compared to refined products. NGLs require high pressure or low temperature to be maintained in their liquid state for shipment and handling. NGLs are highly flammable and necessitate the use of special trucks, ships, and storage tanks.
The volatility of the natural gas liquids somewhat limits the number of markets available for their use. However, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, in 2017, the U.S. exported 1.4 million barrels per day of these liquid gases. The primary export gas was propane which went to 43 countries including Japan, Mexico, China, and South Korea.
Also, as production increases so too do the need for processing plants that separate NGLs from natural gas.
Pros
NGLs are used in petrochemical feedstock that is turned into various chemical-based products.
NGLs have many applications including use as home heating, plastic production, and as a fuel.
NGLs are more widely available with advancements in drilling techniques.
NGLs offer oil and gas companies additional revenue streams.
The U.S. has a growing export business in natural gas liquids.
Cons
NGLs are expensive to handle, store, and transport requiring special trucks, storage, and equipment.
NGLs require high pressure or low temperature to maintain their liquid state for shipment.
Increased NGL use has led to increased demand for processing plants that separate NGLs from natural gas.
Their volatility limits the number of natural markets available for their use.
Real World Example of NGLs
Exxon Mobil Corp. (XOM) is one of the largest producers of natural gas in the U.S. As an example, let's say that a new production facility opened in Texas whereby drilling for natural gas has resulted in a significant amount of the fuel. The gas is extracted from the well and sent to a production facility to be heated at various temperatures to generate the NGLs ethane and propane.
The ethane is removed from the natural gas stream after it reaches the necessary boiling point followed by propane, which is a heavier gas resulting in a lengthier boiling process. Once the propane and ethane have been removed from the natural gas stream, in a process called fractionation, the NGLs travel via a pipeline.
Eventually, the NGLs are shipped by specialized trucks to commercial businesses, industrial plants, and the local gas company. The propane can be used for residential and commercial heating as well as cooking. The ethane is used to create plastics such as water bottles and plastic bags.



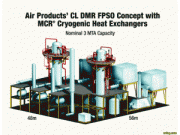
 Understanding Natural Gas Liquids
Understanding Natural Gas Liquids